Web Development Code Languages 2026: A Roadmap for Beginners
Learn the top Web development Code languages. Our guide covers the roadmap from HTML, CSS, and JS to React, Node.js, and SQL for full-stack success. Web development is a rapidly growing field that involves building websites and web applications. It is a complex process that requires knowledge of various programming languages, frameworks, and tools. In this article, we will explore the most common languages and tools used in web development. Stepping into web development in 2025, 2026 is like walking into a massive, bustling city. It’s exciting, full of opportunity, but it’s hard to know which street to take. This world is built on two core pillars: the Front-End (the visible storefront you interact with) and the Back-End (the hidden warehouse and logic that makes it all work). Whether your goal is to be a specialized front-end or back-end developer, or a full-stack expert who builds both, this roadmap will guide you through the essential languages and tools, from day-one basics to job-ready skills.
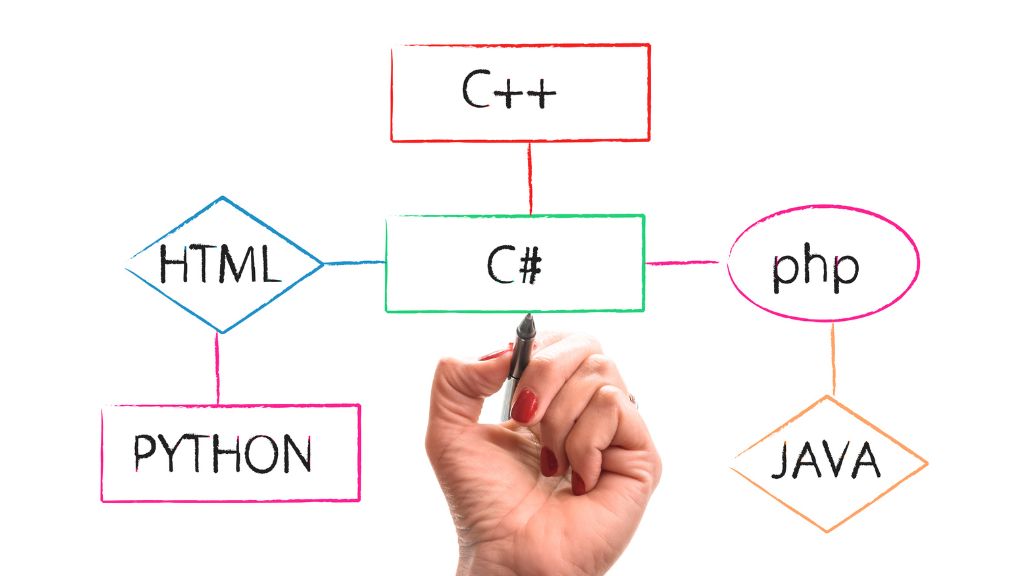
Part 1: The Foundation (The “Front-End Trio”)
Every single website, from a simple blog to a complex app like Google Maps, is built on three core technologies. You cannot skip these. They are the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), the protocol that browsers use to request and receive information.
- HTML (Hypertext Markup Language): This is the skeleton of your website. It’s not a programming language but a “markup” language that defines the structure and content, such as headings, paragraphs, images, and links.
- CSS (Cascading Style Sheets): This is the skin and style. CSS controls everything visual: colors, layouts, and fonts. This is where you’ll implement responsive design, ensuring your site looks great on a phone, tablet, and desktop. You’ll also use it to add custom typefaces (like from Google Fonts) or icon packs (CSS icons). Frameworks like Bootstrap or W3.CSS can help you build beautiful, responsive layouts quickly.
- JavaScript (JS): This is the brain of the site, making it interactive. When you click a button, see a popup, or watch a slider move, that’s JavaScript in action. It’s the first true programming language you’ll learn. It allows you to directly manipulate the HTML DOM (Document Object Model) to change content live.
With just HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, you can build impressive static websites and add interactivity. You’ll learn to fetch data using techniques like AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) or, more commonly today, with JSON (JavaScript Object Notation), which is the standard format for data exchange. While older libraries like jQuery and W3.JS simplified these tasks, modern JavaScript (version ES6+, not the ancient ES5) has adopted many of their features, making them less essential than they once were.
Part 2: Modern Front-End Frameworks
Once you’re comfortable with JavaScript, you’ll find that building complex applications is difficult. This is where JavaScript frameworks and libraries come in. In 2025, knowing one of these is non-negotiable for a front-end job.
- React: Developed by Meta (Facebook), React is the most popular library for building user interfaces. It’s fast, component-based, and has a massive community.
- Vue.js: Known for its gentle learning curve and excellent documentation, Vue.js is a progressive framework that is a favorite for both startups and large companies.
- Angular: This is a full-fledged framework from Google, not to be confused with its predecessor, AngularJS, which is now obsolete. Angular is a powerful, all-in-one solution for large-scale enterprise applications.
- Svelte: The new, hot contender that is gaining massive popularity. Svelte is a compiler that writes highly efficient vanilla JavaScript, resulting in blazing-fast apps.
You’ll also use these frameworks to integrate powerful third-party services, like adding interactive Google Charts for data visualization or embedding Google Maps.
Part 3: The “Engine Room” (Back-End & Full-Stack)
The back-end is the part of the website you don’t see. It handles user authentication, database management, and the core business logic.
- Back-End Languages: You need a language to run on the server. The most popular choice for Full-Stack JS developers is Node.js, which is just JavaScript running on a server. Other top choices in 2025 include Python (with its Django or Flask frameworks) and PHP (which still powers over 70% of the web, thanks to WordPress).
- Databases: This is where your data lives (user info, blog posts, etc.). The most common database language is SQL (Structured Query Language), which is used to manage relational databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL.
- Data Formats: As mentioned, your back-end will send data to your front-end, almost always using JSON. You may also encounter XML, an older but still-used data-interchange format.
Part 4: The Essential Developer Toolkit
Writing code is only half the battle. To be a professional developer, you must use the same tools as the pros.
- CLI (Command Line Interface): You’ll need to get comfortable working in a text-based terminal. It’s faster and more powerful than a graphical interface for many tasks.
- npm (Node Package Manager): This is the world’s largest software registry. It’s a command-line tool you’ll use to install and manage all the frameworks and libraries (or “packages”) your project depends on.
- Git & GitHub: Git is the industry-standard version control system. It’s like a “save” button on steroids for your code, allowing you to track every change and collaborate with a team. GitHub is the most popular website for hosting your Git projects, collaborating, and building your portfolio.
Finally, your site needs a home. This is where cloud platforms like Amazon AWS come in. AWS offers a huge range of services, from simple virtual servers (AWS EC2) to managed databases (AWS RDS), giving you the power to deploy and scale your application for a global audience.





